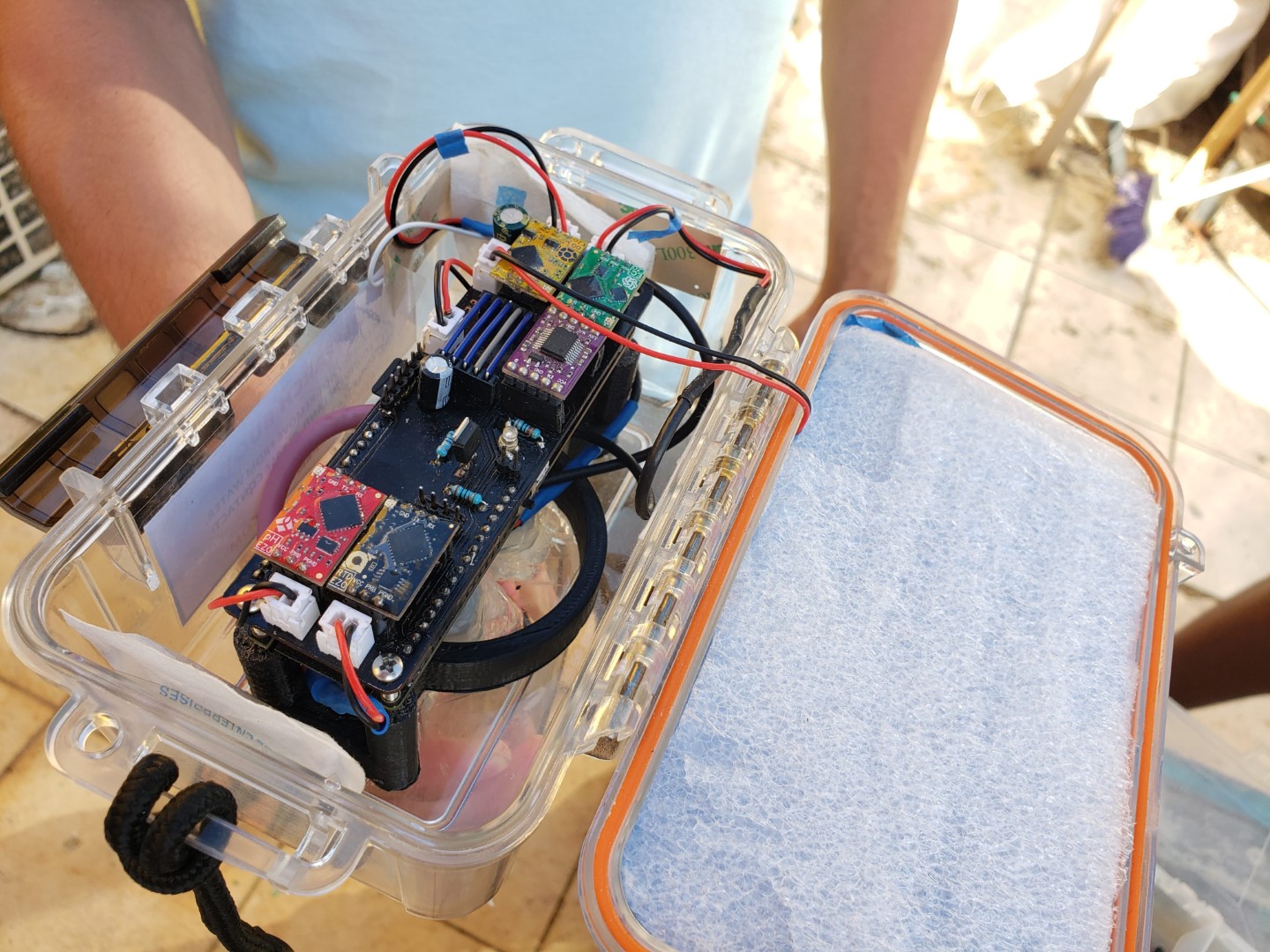
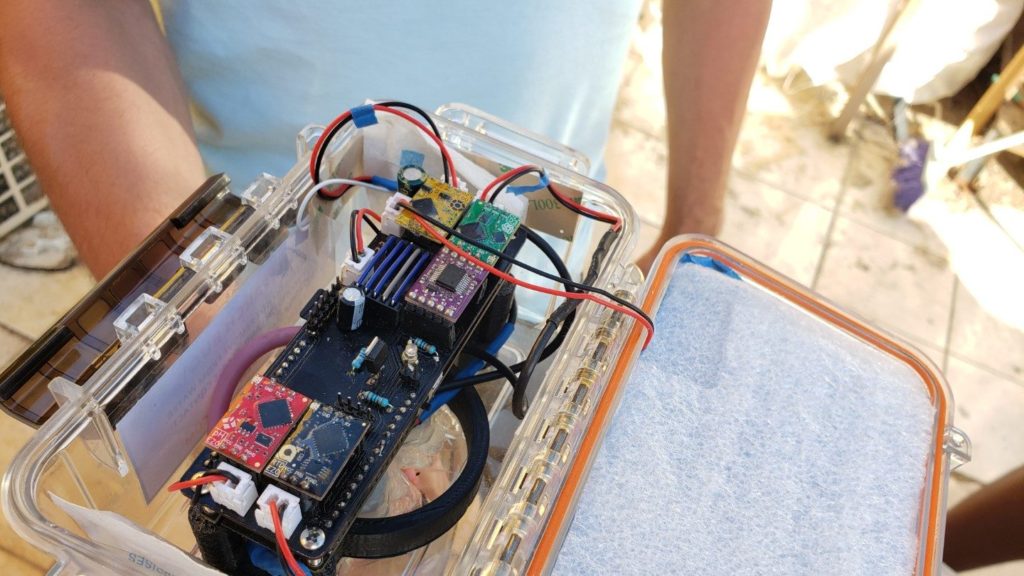
The water quality monitor collects and reports measurements from sensors suspended in the ocean. Currently we are upgrading our prototype and plan to have it back at Surfside in a week or so.
Expanding on our previous water quality experiments, this effort seeks to develop a system for continuous monitoring of aquatic environmental parameters that can be installed off grid, powered by solar panels and communicating through GSM networks. Once operational, this system will be tested against commercial water quality meters and standardized monitoring methods to validate its accuracy.
During a two-month coding extravaganza, Manuel and Sean built the SurfsideSensors repository and prototype environmental monitoring stations for water and air quality. The stations use the same code, with different libraries and deployments for different sensors.
The water quality station, named WAP (water assessing probes), makes use of affordable and high precision probes manufactured by Atlas Scientific. For this station, the included probes measure temperature, pH, electrical conductivity, and dissolved oxygen. Each probe uses a signal interpreting communication circuit that takes the raw signal from the probe, and sends it to the microcontroller on request. The microcontroller that was used includes an onboard battery holder, solar panel port, gps receiver, SD card slot, and a GSM modem with SIM card. This avoids having to find and buy all of these components separately and reduces risk of wiring something up wrong. The enclosure was inspired by the design of MakerBuoy, which uses a watertight utility box and a bottom tube to keep it upright and protect the probes.
The initial development focused on software, followed by construction of a custom circuit board to mount the components. The enclosure was produced last, and the prototype was calibrated and installed on August 22 at Surfside Marina. The unit worked as expected except for the readings of the pH sensor, which fluctuated a lot and reported readings that didn’t make sense for ocean water. After two weeks the unit was removed from the water and inspected. Attempts to recalibrate didn’t work as expected, so we thought that the sensor might have been damaged or defective. Biofouling was observed on the device, which was a concern from the start. Awaiting a replacement pH sensor and restocking of calibration fluids, WAPv1 is currently back at the lab for servicing.
Coming Soon Manual to build water quality sensor
Coming soon link to DATA
Kiko ta oxigeno disolvi?
Manera den aire, tin oxigeno den awa tambe, pero den forma disolvi. Mescos con salo ta mix den awa, oxygeno ta disolve den awa. Esaki ta un importante aspecto pa midi dor cu e nivel di oxigeno disolvi ta afecta bida bao awa. Esaki ta paso cada mata, pisca y tambe mayoria otro bida bao awa mester di oxigeno pa por sobrebibi, pero e unico manera pa haña oxigeno ta den forma disolvi.
Di unda e oxigeno ta bin? Tin dos manera principal cu ta contribi na oxigeno dissolvi. Paso tur substancia semper kier bai di un concentracion halto pa uno mas abao bo ta hanja cu oxigeno ta wordo transferi y absorba door di lama for di aire. Bo por imagine como si fuera bo ta den un camber yen di hende, tur preta riba otro, y tin un otro camber na banda unda si tin lugar, naturalmente hende lo purba di move pa e camber mas bashi. Asina e oxigeno den aire y awa tambe ta traha. Dus oxigeno di aire ta drenta awa paso tin mas lugar.
Mas un cu absorbtion for di aire, oxigeno ta ta bin for di photosynthesis. Nos mata ta captura y usa e luz di solo y e dioxido di carbon CO2 for di aire pa produci entre otro oxigeno. Awel no ta solamente matanan for di tera, pero tamb den awa tin varios organismo cu por traha cuminda for di photosynthesis. Vegetation aquatico, manera yerba di lama, y phytoplankton (tambe conoci como microalga) cu ta inclui entre otro cyanobacteria (un tipo di bacteria) y alga tur ta esencial pa produccion di oxigeno riba nos planeta, den e proceso di photosynthesis ta crea oxigeno cu directamente ta disolvi den awa. E ta importante pa sa cu intercambio di oxigeno entre lama y aire ta pasa constantemente, dus no solamente lama ta absorba oxigeno for di aire pero tambe e ta manda oxigeno back pa e aire, especialmente pa motibo di e production halto di oxigeno for di photosynthesis.
Kiko ta pasa cu e oxigeno den awa?
Wel manera nos riba tera, den awa tambe tur cos cu ta biba mester di oxigeno. Hasta cu oxigeno sa sali for di e awa y bai den aire, semper tin un suma di oxigeno disolvi cu ta keda den awa. Pero e suma ta depende no solamente riba e cantidad di oxigeno den aire pero tambe riba cuanto salo y e temperatura tin den awa. Paso salo tambe ta ocupa lugar den awa, como si fuera e ta competi cu oxigeno pa espacio, asina e ta bira mucho preta pa oxigeno disolvi ora tin mucho salo den awa. E salinidad (cantidad di salo den lama) halto ta causa cu e oxigeno ta sali for di e awa bai den aire cu ta laga e awa cu menos oxigeno. Un otro manera cu oxigeno disolvi por wardo afecta, ta ora temperatura ta laga e molecule di oxigeno disolvi vibra y move rond mucho duru, cu tambe ta hacie facil pa oxigeno por escapa/sali for di awa.
Pakiko worry over di oxigeno disolvi den nos lama?
Paso corda cu tur cos cu ta bibo riba of bao awa mester di oxigeno pa biba. Dus sciencia ta midi oxigeno disolvi pa wak con saludabel e awa di lama ta. pisca y atanan bao awa ta adopta na diferente nivel di oxigeno disolvi. Pesei bo ta haña differente pisca den differente area di awa. Por ehempel un Salmon mester di hopi oxigeno disolvi, dus e ta biba den area cu e temperatura di awa ta mas frieuw. Pero un guppy no mester tanto oxigeno disolvi dus por biba den un area cu temperatura mas halto.
Apart di tur esei tin un proceso cu ta yama eutroficacion. Esaki sa pasa naturalmente pero awendia ta pasa hopi por di actividad humano. Eutroficacion kiermen hopi nutriente (voedingstofnan). Ta drenta den lama manera nitrogeno y fosforo cu ta zorg pa hopi crecimento di cyanobacteria y alganan. Awo bo lo puntra pakiko esaki ta malo? nan ta produci oxigeno disolvi toch? Awel e cos ta, manera tur cos den naturalesa, tur ta depende riba balans. Si tin mucho hopi alga ta crece nan ta competi cu vegetacion aquatico door di tapa e luz, esaki ta causa cu e awa ta bira scur, matando e vegetacion, tambe e alga ta surpasa su mesun limitenan y ta muri tambe. Ora matanan y alganan ta muri den cantidad e ta causa e proceso di decomposicion. E decomposicion of putrimento den otro palabra ta consumi hopi di e oxigeno disolvi, cu no ta laga sufficiente oxigeno pa e pisca nan. Finalmente, e piscanan y otro bida marino ta muri, cu ta causa mas decomposicion ainda, y den su turno agotando casi tur e oxigeno disolvi den e awa.